Blackspot is the most important disease in apple production.
Each rain event has to be judged for its consequences throughout the growing season. Exact timing and the right choice of fungicide and dose are necessary to be effective and economical, and to avoid fungicide resistance and unnecessary residues on fruit.
RIMpro is an internet based decision support system (DSS) for pest and disease management in fruit and grape production.
The platform is used worldwide by producers and their consultants. Besides blackspot, it includes models for codling moth, fireblight and apple canker.
More pest and disease models for apple and other crops will soon be added to the platform. These models are developed in cooperation with experts and working groups, and validated under different climatic conditions. The continuous development of the platform is driven by feedback from users and new scientific information.
Inputs
The system inputs are weather data from an on-farm weather station, and high-resolution weather forecast data for your location.
Simulation models process these climate data and output clear graphics that show the development of pests and diseases in your crop.
The infection process
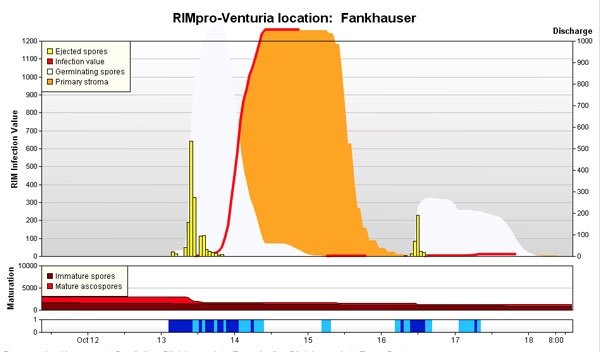
Figure 1 shows an example of an infection event spring 2014.
Rain started during the night of October 13 (dark blue in the lower graph). As long as it is dark, ascospores discharge is low (yellow bars). When the sun comes out and rain continues, ascospore discharge peaks and continues for several hours.
The pool of germinating ascospores on the leafs is show as a white cloud. This ‘germination window’ is the only moment where contact fungicides such as Captan and Delan can interrupt the infection.
The red line marks the stage where the spores infect the leaves and are no longer depending on free water on the leaf surface.
After the red infection line, contact fungicides are no longer effective.
The orange area is the time frame where fungicides with limited curative efficacy still can be used. These are Dodine for integrated production, and lime sulfur or potassium bicarbonate in organic apple production. Modern systemic fungicides can be applied for a longer time after infection in orchards, were resistance against these fungicides has not been found.
Rain on October 16 again triggered discharge of some ascospores. As the leaf wetness duration (light blue in the lower graph) was not sufficient, these spores died without causing infection.
Evaluating your fungicide schedule (continued next month)
For more information, see Tree Fruit August 2015