Apple Scab is the key disease in apple production.
Either measured in potential economic loss or costs and efforts necessary for its control. The apple scab model available on the RIMpro Cloud Service has proven its value over the past 20 years.
For Australia, this service is offered by Marcel Veens Horticultural Adviser Pty. Ltd.
The apple scab fungus rules the life of fruit growers and their advisers.
Every rain event has to be judged for its consequences. Mostly there is only one right decision to make, and only one moment for the perfect application.
Uncertainty leads to more fungicide treatments than necessary or damage by scab. So in either case to higher costs.
RIMpro helps to make the best decisions. Graphs show the current situation and the development in the coming hours and days using local weather forecast.
The service offers the possibility to register spray schedules, and estimate the cover remaining from the last fungicide treatment.
Understand the infection process
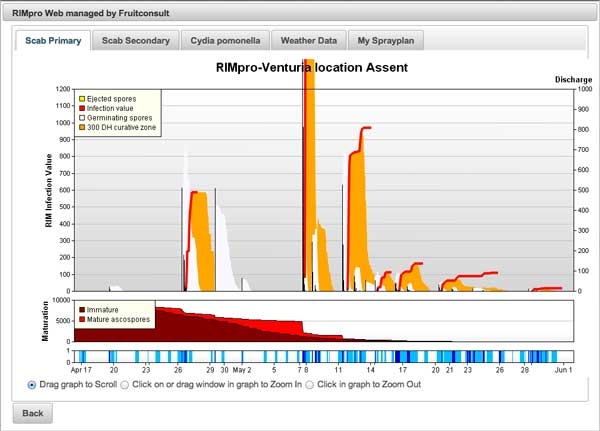
The RIMpro graph shows the relative importance of primary scab infections. (Figure 1, example from Europe).
Three high peaks mark the major scab infections, followed by a few smaller ones.
Infection values under 100 are considered light; up to 300, moderate; over 300 is a severe infection risk. Scab infections with RIM values over 600 occur only a few times per year and are the key infections.
Inadequate management of these infections undoubtedly leads to scab damage.
Figure 2 shows an infection event in detail. In the middle graph you see in red, the proportion of the ascospore potential ready to be ejected during next rain. The actual spore discharge is presented as yellow bars.
The following ‘white cloud’ in the graph represents the spores that try to germinate. Depending on the temperature it takes them up to 40 hours to germinate and infect the leaf.
When leaf wetness stops earlier the spores survive for some time, but eventually die without infecting the leaf. This happens in the example to the spores discharged on April 29.
When wetness continues the spores germinate and penetrate the leaf. This is the moment of infection (red line). The more spores infect the leaf the more severe the infection, and the higher the RIM value.
Once under the cuticle the fungus starts growing. The first 200-300 Degree Hours (DH) the mycelium is still small and vulnerable. Products like Dodine, Lime Sulphur and Potassium Bicarbonate can still kill the fungus and stop the infection. This stage is the orange zone following the red infection line in the graph.
At what stage do fungicides work (continued next month)
See this article and images in Tree Fruit July 2014